 Sun
power
(solar power) can make electricity by using things called Sun
power
(solar power) can make electricity by using things called  photovoltaic
cells (often just called PV – easier to say) which fit on the
roofs or walls of your houses or apartment blocks. Some special cars
can run on PV electricity and there’s even a race across Australia
in which the cars run only on solar power photovoltaic
cells (often just called PV – easier to say) which fit on the
roofs or walls of your houses or apartment blocks. Some special cars
can run on PV electricity and there’s even a race across Australia
in which the cars run only on solar power |

PV panels on a house in
the USA |
 Sun
power can heat water in solar panels
(like radiators but instead of giving out heat, they grab it from
the Sun). This is then stored in a big tank so you can have hot showers
and so on. Solar collectors can pick up the sun's heat even on cloudy
days Sun
power can heat water in solar panels
(like radiators but instead of giving out heat, they grab it from
the Sun). This is then stored in a big tank so you can have hot showers
and so on. Solar collectors can pick up the sun's heat even on cloudy
days |

Solar hot water panels on
a hotel roof in Greece |
 Solar
power can also directly heat houses in cold
countries – when they’re properly designed to make best use of it.
So far, not many are. This is called passive solar energy Solar
power can also directly heat houses in cold
countries – when they’re properly designed to make best use of it.
So far, not many are. This is called passive solar energy |

This glass conservatory
captures the sun's heat and warms this farmhouse in Wales
|
 Hydroelectric
power
makes electricity by using the energy from falling water. The water
comes from big dams across rivers, and flows down great tubes to drive
electricity generators. Most of the world’s biggest rivers are already
used for this Hydroelectric
power
makes electricity by using the energy from falling water. The water
comes from big dams across rivers, and flows down great tubes to drive
electricity generators. Most of the world’s biggest rivers are already
used for this |

The Three Gorges Dam in
China is the largest hydro-electric power station in the world |
 Wind
power
can drive a turbine with a propeller (like some airplanes have) and
make electricity. Wind power is getting really important in some countries. Wind
power
can drive a turbine with a propeller (like some airplanes have) and
make electricity. Wind power is getting really important in some countries.
 Here's
a cartoon video (like Wallace and Gromit!) about wind turbines
which I rather like! Here's
a cartoon video (like Wallace and Gromit!) about wind turbines
which I rather like! |

A big wind turbine in
Denmark. Can you make out the door at the bottom?
|
  Wave
power
can also drive generators but this is still a very new idea. Just
a few experimental machines are in use today. Wave
power
can also drive generators but this is still a very new idea. Just
a few experimental machines are in use today. |

Pelamis wave machine in
operation off Portugal
|
 Tides – you know, when the sea goes up and down twice a day – can drive
generators too. There's just one example of this in action at a place
called La Rance in France. Other parts of the world with big tides
could be useful too, but a big dam has to be built to trap the moving
seawater Tides – you know, when the sea goes up and down twice a day – can drive
generators too. There's just one example of this in action at a place
called La Rance in France. Other parts of the world with big tides
could be useful too, but a big dam has to be built to trap the moving
seawater |

Tidal power plant on the
estuary of the Rance River, Bretagne, France |
 Biogas
(methane) for cooking and heating can be made from human sewage and
farm animals' waste. (Phew! Yuk! … but very useful.) It's made in
special tanks called biodigesters. Landfills – that's where people's
garbage gets dumped – also produce methane gas as the rubbish rots.
Usually this is collected and used to make electricity Biogas
(methane) for cooking and heating can be made from human sewage and
farm animals' waste. (Phew! Yuk! … but very useful.) It's made in
special tanks called biodigesters. Landfills – that's where people's
garbage gets dumped – also produce methane gas as the rubbish rots.
Usually this is collected and used to make electricity |

A working biodigester on
a farm in Germany |
 Biofuels:
Because plants and trees soak up CO2 like sponges,
making the carbon into wood and putting back oxygen into the air,
people can ‘grow’ fuel without adding CO2 pollution to
the air. It's called 'carbon neutral'. In Brazil, people pioneered
growing sugar cane plants to make alcohol which they use to power
almost half the country’s cars. In other countries, people plant
special trees (like willow) which grow fast and you can cut them
down without killing them – so they keep on re-growing. This is
called coppicing. You can use the wood for burning to make heat
as well as other things. Biofuels:
Because plants and trees soak up CO2 like sponges,
making the carbon into wood and putting back oxygen into the air,
people can ‘grow’ fuel without adding CO2 pollution to
the air. It's called 'carbon neutral'. In Brazil, people pioneered
growing sugar cane plants to make alcohol which they use to power
almost half the country’s cars. In other countries, people plant
special trees (like willow) which grow fast and you can cut them
down without killing them – so they keep on re-growing. This is
called coppicing. You can use the wood for burning to make heat
as well as other things.
Other
biofuels like ethanol
and palm
oil seemed like a good idea at first but they've turned out
to be a bit of a disaster. Why? |

Sugar cane, cut and ready
for processing

Ethanol is a type of alcohol. To make it, people are turning food crops like maize (corn) into fuel instead of food.

Palm oil comes from vast plantations of oil palms in some tropical countries.
|
  Fuel
cells
make electricity directly from hydrogen, a very light gas. The cells
don’t burn the hydrogen. Instead it reacts with oxygen (in the air)
to make electricity. The only ‘waste’ is water. Soon cars will run
with fuel cells powering electric motors so they are silent and make
no pollution. They can also make power for houses so there’d be no
need for big polluting power stations. One way people can make hydrogen is by using sunlight to split water into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Scientists are still searching for a good way to do this. Fuel
cells
make electricity directly from hydrogen, a very light gas. The cells
don’t burn the hydrogen. Instead it reacts with oxygen (in the air)
to make electricity. The only ‘waste’ is water. Soon cars will run
with fuel cells powering electric motors so they are silent and make
no pollution. They can also make power for houses so there’d be no
need for big polluting power stations. One way people can make hydrogen is by using sunlight to split water into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Scientists are still searching for a good way to do this.
 Problems with hydrogen
Problems with hydrogenHydrogen when mixed with air is highly explosive. It is also very difficult to store which is a big problem if it is to be used for powering transport. And producing it needs a lot of electrical energy.
|

A hydrogen fuel cell public
bus in Australia |
 Geothermal
energy is
energy tapped from inside the Earth. It's the only renewable energy
source which has nothing to do with the Sun. Deep down, it's very
hot. Sometimes these hot rocks break through the surface to form volcanoes.
By drilling holes down into areas where hot rocks are close to the
surface, people can generate electricity and heat buildings. One type
of geothermal energy uses Geothermal
energy is
energy tapped from inside the Earth. It's the only renewable energy
source which has nothing to do with the Sun. Deep down, it's very
hot. Sometimes these hot rocks break through the surface to form volcanoes.
By drilling holes down into areas where hot rocks are close to the
surface, people can generate electricity and heat buildings. One type
of geothermal energy uses  geothermal
heat pumps to make hot water for home heating. A heat pump is
a sort of reversed refrigerator. A different sort of geothermal
heat pumps to make hot water for home heating. A heat pump is
a sort of reversed refrigerator. A different sort of 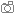 heat
pump takes its heat from the air outside a house and warms the
air inside. Sounds impossible, doesn't it, but it works! heat
pump takes its heat from the air outside a house and warms the
air inside. Sounds impossible, doesn't it, but it works! |

Geothermal power plant in
Iceland |

